EZ Pilot
Autopilot
The EZ Pilot
is a single axis (roll control) autopilot
|
Extreme altitude, very thin air, temperature of -66 degrees F, and the EZ Pilot worked flawlessly during the arduous flight. "The EZ Pilot continued to operate normally,” Bohannon said. “Once I determined that the plane wasn’t capable of going any higher, I just hit the Mode button to see if the automatic 180 degree turn feature would work, and it took me back home while I descended. Even at that extreme altitude and temperature it worked exactly as advertised.” |
The EZ Pilot includes the
Gold Standard servo

Servo Installation Kit = $55
|
The pilot simply enters a flight plan into the GPS and presses the Servo button. The EZ Pilot then precisely tracks the flight plan.
If the pilot wishes to deviate from the programmed flight path, the Mode button is pressed to enter the Course mode and track any bearing selected with the "L-R" switch. The new bearing will display on the readout and the aircraft will track that bearing.
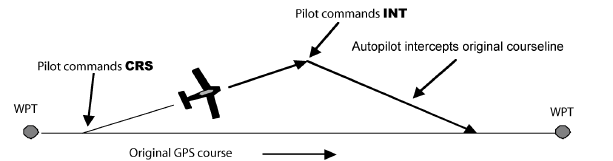
An Intercept mode (with adjustable intercept angle) is available to steer the plane back to the original flight path.
A remote Servo Disconnect switch provides instant release of flight controls. Holding the switch down for three seconds or more enables Pilot Command Steering. This allows the pilot to manually fly the aircraft to any new heading and, upon releasing the switch, the autopilot will track that course. A convenient Display switch allows the pilot to read the Waypoint Designator, Ground Speed, Distance to Waypoint, Time to Waypoint, Crosstrack error, Track Offset Position and a graphic Turn Coordinator. Three navigation modes provide maximum flexibility: 1. Track mode (TRK) – used for area navigation tracking a host GPS flight plan (or GOTO data).
2. Course mode (CRS) - provides vector navigation as illustrated below. CRS also allows tracking a specific pilot-selected course when the host GPS route function is not in use. CRS mode uses the GPS signal to provide the aircraft groundtrack.
3. Intercept mode (INT) – used to intercept a predefined GPS desired track (DTK) as illustrated below. The INT mode also uses the GPS signal to provide the aircraft groundtrack.
|

 Bruce Bohannon has flown his "Flyin' Tiger" to an
altitude of 47,530 feet,
Bruce Bohannon has flown his "Flyin' Tiger" to an
altitude of 47,530 feet,